05. Specificity
Specificity Heading
Specificity
ND001 C01 L02 04 Specificity
Specificity
Because elements can have multiple CSS selectors, there is a hierarchy for the weight given to each type of selector. Here is the logical order of selectors from least to most weight assigned:
- Type selectors (e.g., h1) and pseudo-elements (e.g.,
::before). - Class selectors (e.g.,
.example), attributes selectors (e.g.,[type="radio"]) and pseudo-classes (e.g.,:hover). - ID selectors (e.g.,
#example).
This concept can help you understand why your styles aren't being applied in the way you expect.
There is a way to escape or override the specificity evaluation of elements using the !important keyword after an individual CSS property rule, but a couple important reminders:
Always look for a way to use specificity before even considering !important.
Never use !important on site-wide CSS.
Image - Specificity1

Specificity levels
Image - Specificity2

Specificity explanation - example
Specificity3
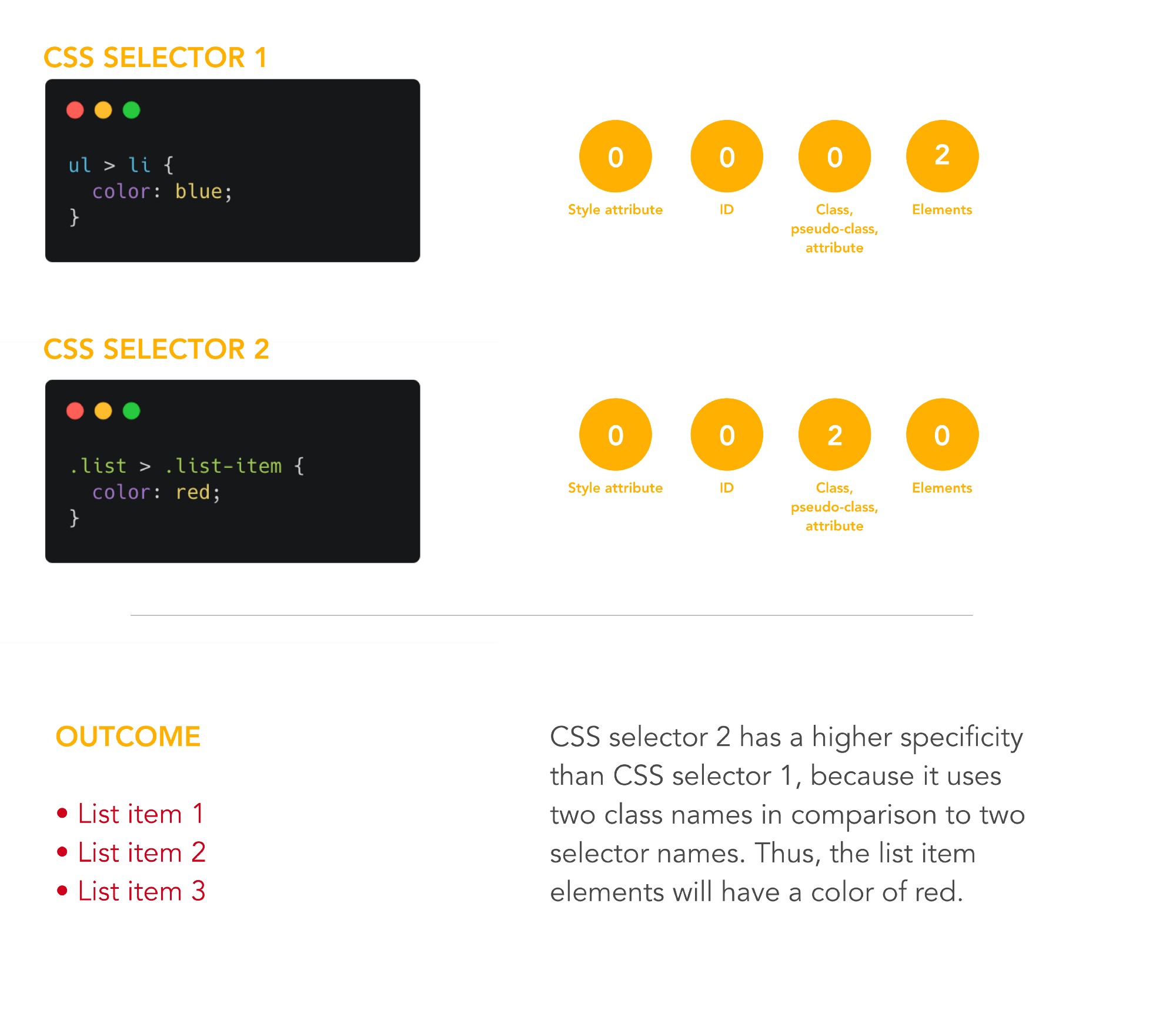
Specificity explanation - example
Quiz 3 - Specificity